
Last month, Sen. John McCain died from glioblastoma, a form of brain cancer. The same disease took the life of Sen. Edward Kennedy.
But here in Oklahoma, Norman’s Mike Schuster continues to live with the disease. As he nears the three-year anniversary of his diagnosis with the deadly cancer, he’s already doubled the life expectancy for patients with glioblastoma.
Doctors can’t say why Schuster has lived where others have succumbed to the disease. But they believe it may be because of an experimental drug he received—one that was developed by scientists at the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation.
For Schuster, the first clue that something was awry came in the fall of 2015, just past his 50th birthday. While at work, he passed out with no warning.
He was rushed to the hospital, where an MRI revealed a brain tumor the size of a kiwi just above his right eye. “I’d been healthy all my life,” Schuster said. “No medical issues at all. I just couldn’t believe that this was happening.”
Of the more than 120 types of brain and central nervous system tumors, Schuster’s type, known as a glioblastoma, is the most aggressive. The standard treatment regimen involves surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by radiation and chemotherapy. Still, the tumor almost always grows back.
With treatment, the median survival—which means half of patients live longer, and half die sooner—is 12 to 18 months. Only 1 in 20 glioblastoma patients will live five years.
In a procedure that lasted six hours, doctors removed as much of Schuster’s tumor as they could. When Schuster regained consciousness, his surgeon explained that he’d succeeded in excising most of the tumor. But, he said, like most glioblastomas, this one had “tentacles.” Tiny arms of the tumor had grown into surrounding brain tissue and could not be removed.
Schuster began follow-up radiation treatment at the Stephenson Cancer Center at the University of Oklahoma. Even though Schuster couldn’t feel the electromagnetic waves pulsing through his brain, “you could smell it,” he said. He also started chemotherapy, taking a pill called temozolomide. Together, the treatments were intended to kill the tumor cells that remained in the fissures of his brain.
“If you leave even a single cancer cell in the brain, it can regrow,” said Dr. James Battiste, the neuro-oncologist who oversees Mike’s care at Stephenson. “The brain is fertile soil for these tumors. That’s why chemo and other therapies are so important.”
Following radiation—doctors limited his treatment to six weeks for fear of triggering a secondary cancer—Schuster stayed on temozolomide. But just after the one-year anniversary of his diagnosis, an MRI revealed a new tumor.
A second surgery once again removed the primary tumor. This time, doctors kept Mike awake throughout the procedure to ensure they didn’t damage crucial areas of his brain. Still, many glioblastoma tentacles had escaped surgeons’ reach, remaining lodged in Schuster’s brain.
Schuster knew those tentacles were, in essence, seeds that could sprout another full-blown tumor in a matter of weeks. He told Battiste he was willing to try anything to beat back the glioblastoma. He’d read about clinical trials of experimental medications. Was there one that might help him?
Battiste, in fact, was testing a new drug that, he said, “just seemed suited for Mike.” It was an investigational medication for glioblastoma that had been born just down the block from Stephenson, in the labs of the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation.
Known as OKN-007, the experimental medication was discovered by OMRF scientists Drs. Rheal Towner and Robert Floyd. In pre-clinical glioblastoma experiments, the compound dramatically decreased cell proliferation (spread) and angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels), and it turned on the process of removing damaged cells so they can’t become cancerous.
“Those are the three major factors needed in a cancer drug,” Towner said. “This compound seemed to do all of them.”
Oblato, Inc., a New Jersey subsidiary of Korean biotechnology company GTreeBNT, has acquired the rights to OKN-007 from OMRF. It will move ahead with further trials of the drug in glioblastoma.
At Stephenson, Battiste has been cautiously optimistic about the performance of OKN-007 in Schuster and his other patients. “We’ve gone to the highest dosage levels the FDA would allow, and we haven’t seen any negative effects from the drug.” Although evaluating the medication’s effectiveness at stopping the regrowth of tumors is not a primary focus of the early phases of the trial, “it’s helpful to see things looking good” on this front, too, he said.
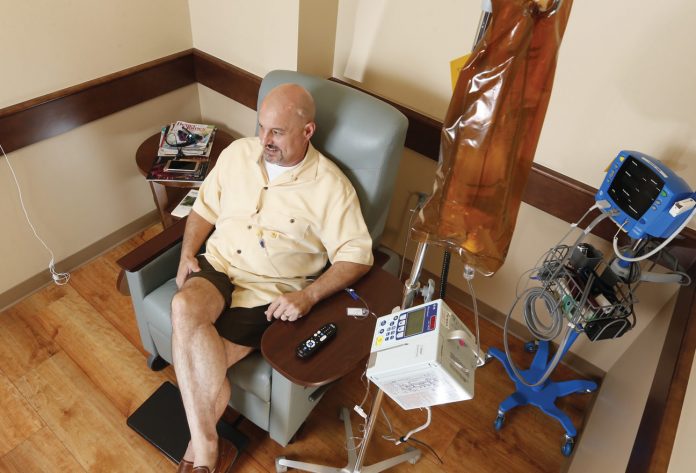
In August, Schuster celebrated his 53rd birthday. When he sees other patients with brain tumors, he said, they appear thin and frail. He, on the other hand, has added 15 pounds since beginning OKN-007 infusions. “I’ve had no side effects at all,” he said. “I’ve also been able to get back to the gym and am doing some yard work. I feel really good.”
He continues to travel to Oklahoma City each week for infusion treatments with OKN-007. “I really appreciate all of the support we’ve received from Stephenson and from people at OMRF,” he said.
While fighting glioblastoma has brought numerous challenges, Schuster said the experience has also revealed silver linings. “My friends and family and their prayers for me have turned into blessings.”
Of course, neither Schuster nor his doctors can know for sure if the drug is responsible for keeping his cancer at bay. Nor can they say if, or when, the disease might recur. “I can’t worry about stuff,” Schuster said, “that’s out of my control.”
Still, he feels certain he made the right decision when he opted to participate in the clinical trial. “Let’s just say I’ve been very blessed. It’s pretty cool how this stuff is working.”












